All the Exercise code can be found here SQL Code
1. create table emp
(
empno char(4),
ename varchar2(25),
sal number(7,2),
city varchar(15),
dob date
);
INSERT into emp
values('2','Kritika','60000','Ranchi','12-Aug-1991');
INSERT into emp
values('3','Shyam','70000','Bangalore','12-Aug-1987');
INSERT into emp
values('4','Rajesh','80000','Patna','12-Aug-1990');
3. DELETE * From emp where dob='12-Aug-1989' //will give error because no table selected
4. DELETE emp where dob='12-Aug-1989';
5. INSERT into
emp(empno,sal) values('1','48000');
6. INSERT into emp
values('1','Atul','48000',null,null); //You can put null values in oracle
7. select * from emp where
city='Ranchi' and sal=60000; //And
operator work like this another operator is NOT AND OR
8. select * from emp where
sal>=60000; //Retional operator is >, >=, <,
<=, != or <> ,=
9. select ename,sal,sal*12
as "Anuual income" from emp; //Computed
field for annual salary
10. select distinct job from emp;
select unique job from emp;
11. select * from tab //all the table will shown present on DB
12. describe emp;
Some extra tables for
future references
13. create table employee
(
empno char(4),
ename varchar2(25),
sal number(7,2),
city varchar(15),
dob date,
job varchar(25),
deptno number(4)
);
create table dept
(
deptno number(4),
dname varchar(25),
location varchar(25)
);
create table dept_head
(
deptno number(4),
dhead varchar(25)
);
create table projects
(
project varchar2(40),
pname varchar2(25),
describe varchar2(25)
);
create table emp_projects
(
project varchar2(40),
empno char(4)
);
13. Order by clause:
For setting the limit of
output in sql command use following
SETSERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE
4000
SET LINESIZE 4000 // IT IS
WORKING IN MY CASE
SET PAGESIZE 4000
SET LONG 4000;
Example : select * from employee order by deptno;
select * from employee order by deptno,job;
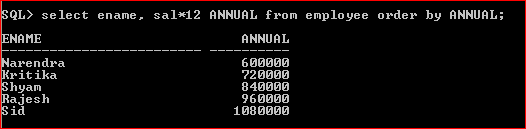
14. select ename, sal*12
ANNUAL from employee order by ANNUAL;
****Always remember that
order by comes after where clause in any query****
****Or you can say order
by is last entity of your query ****

16. select * from employee
where ename >'N' and <'A';
***will show you all the
result after N character and before A character (Filter kind of thing)***

****Special character****
17. select * from employee
where ename like 'K%'

18. select * from employee
where ename like '__d%';

19. select * from employee where ename NOT like
'Nar%';

20. select * from employee
where sal between 60000 and 80000;

21. select * from employee where deptno=10 or deptno=10
or deptno =40;

22. . select * from employee where deptno=any(20,40);

23. select * from employee
where deptno IN(20,40);

****Second one is fastest
query in above of two****
**UPDATE***
24. update emp set
sal=sal+sal*0.2 where empno=3;

To verify:

***DROP will drop one
table at a time***
Drop emp :
***DECODE --> It is the MOST POWERFULL FUNCTION it
works as switch case in db****
25. select decode
(deptno,10,'TEN',20,'TWENTY','OTHERS') from emp;

You can see the power of
DECODE in below query
select ename ,sal,
decode(sign(sal-60000),1,'High Salary',-1,'Low salary','Medium salary') from
employee;
*** GROUP FUNCTION****
***AVG,MIN,MAX,COUNT,SUM,****
26. SELECT avg(sal) from
employee;
27. SELECT min(sal) from
employee;
28. SELECT max(sal) from
employee;
29. SELECT sum(sal) from
employee;
30. SELECT count(sal) from
employee;
***All group function are
very useful to create summary reports.*****
*****GROUP BY FUNCTION***********
Some important rules for
group by
You can not select
ordinary column along with group by function.
you can not select single
row function along with group function.
you can not use group
function in where clause.ction.
31. select deptno
,sum(sal) from employee group by deptno;
*****HAVING
CLAUSE**********************
32.select deptno ,sum(sal) from employee group
by deptno having sum(sal)>70000;

33. select deptno
,sum(sal) from employee group by deptno having count(*)=1;

*******MATRIX
FUNCTION*******
34. select
deptno,count(*),min(sal),max(sal),sum(sal) from employee group by deptno;

35.***************Join*******************
I have following tables to
play with joins .

35. ***************Join*******************
I have following tables to play with joins .
select
dname, ename
from
employee, dept
where
dept.deptno = employee.deptno;
/*Here dept table is Driving table and employee is
driven table it depends on from clause
/* Driven table shd be table with lesser records
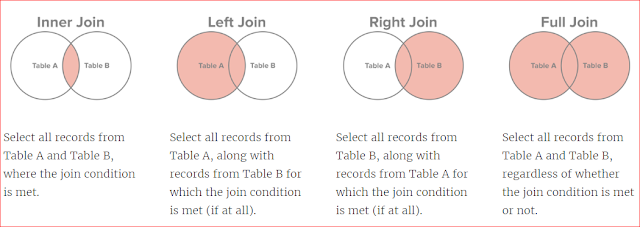
***EQUI JOIN****

Explanation:
Show matching rows of both tables.
+ Non matching rows of
outer table(which is opposite to +sign)
37.
******************Outer Join*******************
Left Outer joins
select
dname, ename
from
employee, dept
where
dept.deptno(+) = employee.deptno;
Right Outer joins
select
dname, ename
from
employee, dept
where
dept.deptno = employee.deptno(+);
FULL Outer joins
select
dname, ename
from
employee, dept
where
dept.deptno (+)= employee.deptno(+);
38. Cartesian Join (Join without any where clause)
select
dname, ename
from
employee, dept
39. Self Join (When parent and child both are present on
the same table .It is slowet join among all)
select a.ename, b.ename
from employee b, employee a
where a.job = b.dob;
40. ******************SET OPERATORS*******************
UNION
select empno, ename from
emp
UNION
select empno, ename from
employee
UNION ALL
select empno, ename from
emp
UNION ALL
select empno, ename from employee

INTERSECT:
select empno, ename from
emp
INTERSECT
select empno, ename from employee;
MINUS :
select empno, ename from
emp
MINUS
select empno, ename from employee;